Detect hand touching objects
Setup Hand
To detect if the right hand is touching an object (e.g., A), both the right hand and object A need a Collider.
Setup hand collider
Under XROrigin > Right Hand > Right Hand Interaction Visual > R_Wrist, add an empty object. In this case, I named it ColliderBox
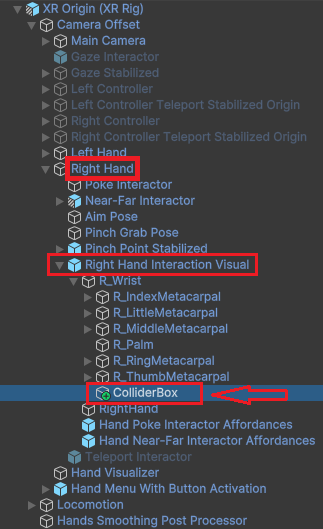
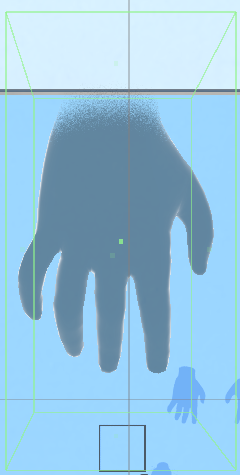
Choose the type of Collider that best surround the object. For the hand, I used Box Collider to cover the whole hand.
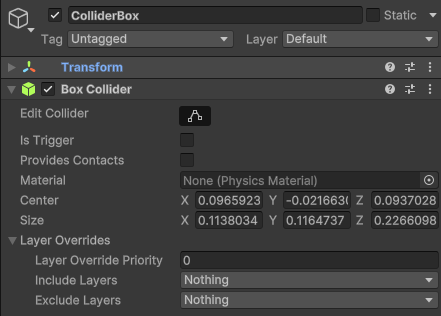
Here's what the collider looks like after configuration:
Setup RigidBody
Why do we need a RigidBody?
- If you want an object to participate in trigger events without physics interaction, you can use a collider with a Rigidbody set to Kinematic. This will allow the trigger events like OnTriggerEnter to work.
- If you want a completely static object that still participates in trigger events, you can use a collider without a Rigidbody, as long as the other object in the trigger has a Rigidbody.
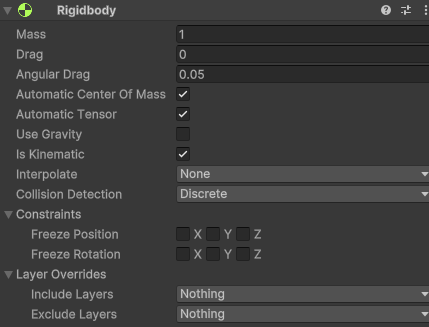
By setting the Rigidbody to Kinematic and disabling Use Gravity, the hand can interact with trigger events while maintaining precise control of its movement.
Configuration Steps:
- Add a Rigidbody to the hand's collider object (e.g., ColliderBox).
- Set Use Gravity to unchecked.
- Set the Rigidbody to Kinematic.
Repeat for the Left Hand
Follow the same steps to configure the left hand.
Setup Dog
Since the dog's body parts move independently, using a single collider (e.g., a bounding box around the entire body) may not work as expected when the dog changes poses (e.g., from standing to sitting). To address this:
- Add colliders to individual body parts (e.g., Capsule Collider for the head, limbs, etc.).
- Enable Is Trigger on each collider to allow OnTriggerEnter, OnTriggerStay, and OnTriggerExit events.
- Assign the same tag (e.g., dog) to all colliders to detect them collectively as the "dog."
For example, here’s how the Capsule Collider around the dog's head is set up:
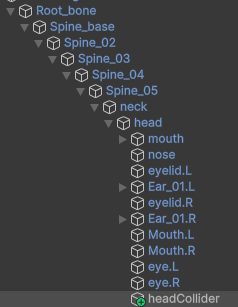
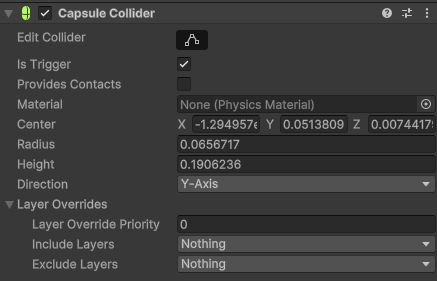

Scripts
Detect When the Hand Starts Touching the Dog
private float startTime = 0f;
void OnTriggerEnter(Collider collider)
{
Debug.Log("Hand touching sth");
if(collider.gameObject.CompareTag("dog"))
{
Debug.Log("Hand touching dog");
startTime = Time.time;
}
}
Detect if the Hand Stays Touching the Dog for 5 Seconds
void OnTriggerStay(Collider collider)
{
if(collider.gameObject.CompareTag("dog"))
{
// gloveController.PlayHapticFeedback();
gloveController.PlayHapticFeedback();
Debug.Log("Hand stay touching dog");
float elapsedTime = Time.time - startTime;
if (elapsedTime > 2f)
{
Debug.Log("User has petted dog for more than 5 seconds!");
// uiPrompt.SetActive(true);
animator.SetBool("idle", true);
if(sequenceHandler.GetIsWaitingForPetting()){
sequenceHandler.IncrementStateIndex();
}
}
}
}
Detect When the Hand Stops Touching the Dog
void OnTriggerExit(Collider collider)
{
Debug.Log("Hand leaving sth");
if(collider.gameObject.CompareTag("dog"))
{
startTime = 0;
Debug.Log("Hand leaving dog");
animator.SetBool("idle", false);
}
}
Key Notes:
- Colliders: Ensure the colliders for the hand and the dog's body parts are properly aligned and scaled to avoid false positives or missed collisions.
- Rigidbodies: At least one of the objects involved in the trigger (hand or dog) must have a Rigidbody for the trigger events to work.
- Tags: Use consistent and specific tags (e.g., dog) to simplify collision detection logic.