Important Concepts
Useful Links:
Angular Overview
In Angular, Components define views—screen elements that are dynamically adjusted based on program logic and data. These components use Services for background tasks like data fetching, which can be injected as dependencies to make your code modular and reusable.
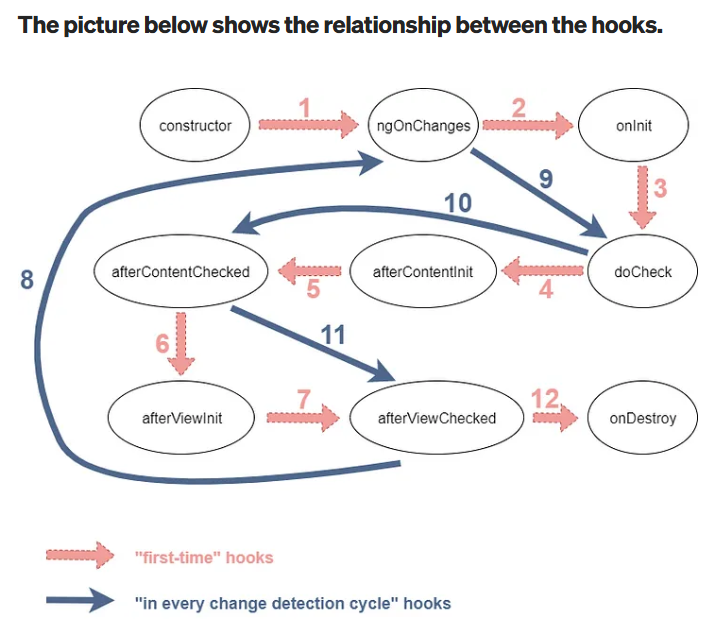
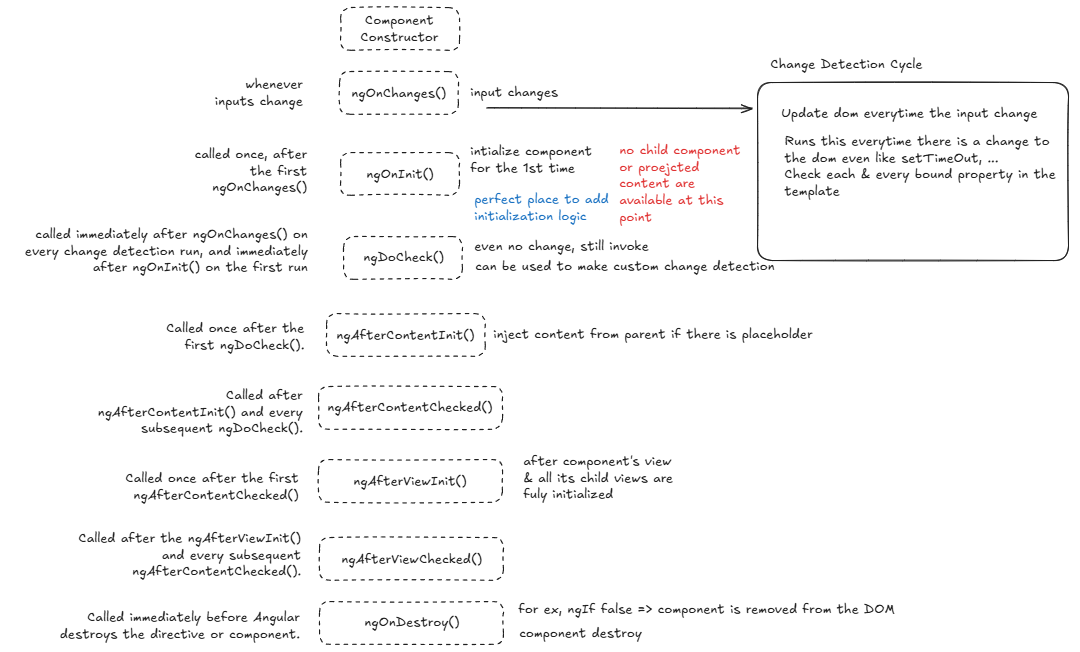
Lifecycle
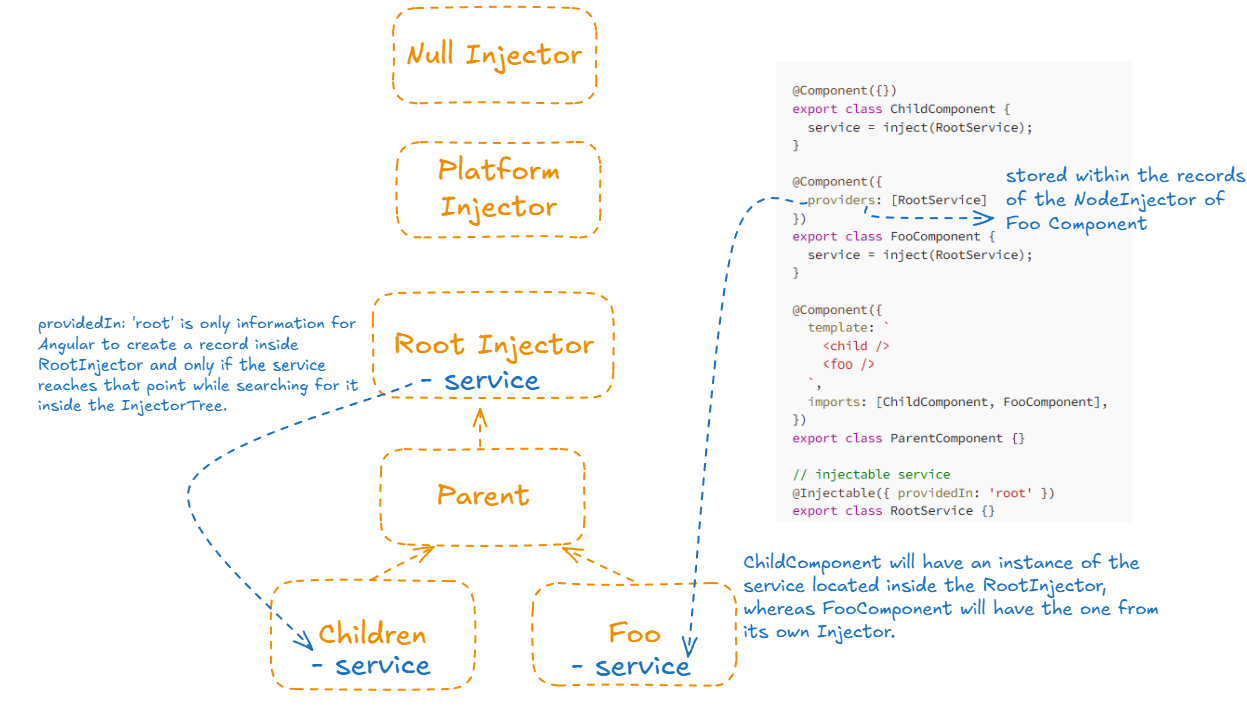
Dependency Injection
When a dependency is requested, the injector checks its registry to see if there is an instance already available there. If not, a new instance is created and stored in the registry.
 Check out this article for in depth explanation
Check out this article for in depth explanation
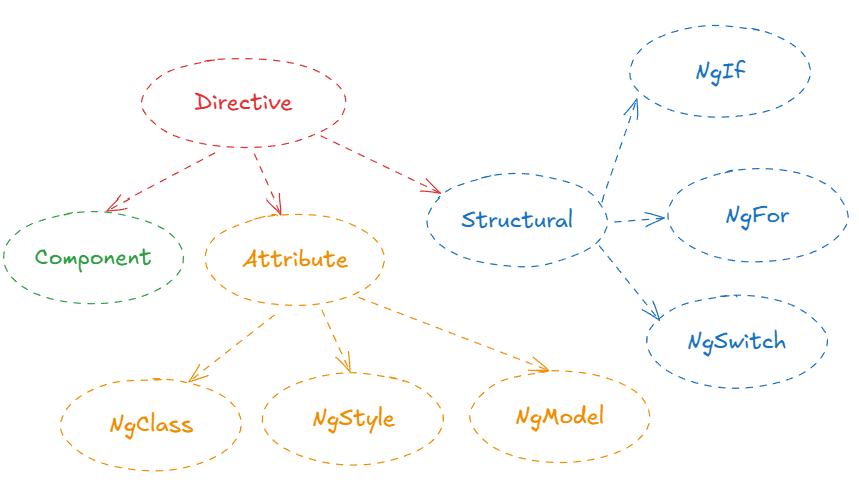
Directives
Decorator
Decorators are functions that modify classes, methods, properties, or parameters in a declarative way.
- Class decorator:
@Component,@Directive, and@NgModule - Property decorator:
@Input - Method decorator: applied to class method. Ex:
@HostListenerallows us to listen for events on a method.
Uses of Decorators in Angular
- Use
@Componentto define the metadata of Angular components, including template, styles, and selector. - Use
@Injectableto make service injectable as a service throughout the application. - Use
@Directiveto attach custom behavior to elements in the DOM. - Use
@Pipeto define custom data transformation logic for templates. - Use @
NgModuleto structure Angular modules and manage dependencies. - Use
@Inputand@Outputto pass data between parent and child components. - Use
@ViewChildand@ViewChildrento access child components or elements in the view.
NgModule
Recommend using standalone components instead of NgModule.
For more info, check out this discussion
NgModule is key building blocks of the framework. It organizes components, services, and other dependencies into cohesive units.
Core libraries like RouterModule, BrowserModule, and FormsModule are NgModules. Angular Material, which is a third party tool, is also a type of NgModule.
A typical NgModule file declares components, directives, pipes, and services. It can also import other modules that are needed in the current module.
importare used to import supporting modules likeFormsModule,RouterModule,CommonModuledeclarationsare used to declare components, directives, pipes that belong to the current module. Everyone inside declarations knows each otherProvidersare used for injecting the services required by components, directives, pipes in the module.export: components, directives, modules or pipes that we would like to have access to them in another module (after importing this module)bootstrap: the root component that Angular creates and inserts into the index.html host web page.
Components are declared, Modules are imported, and Services are provided.
Traditional Web App vs. SPA
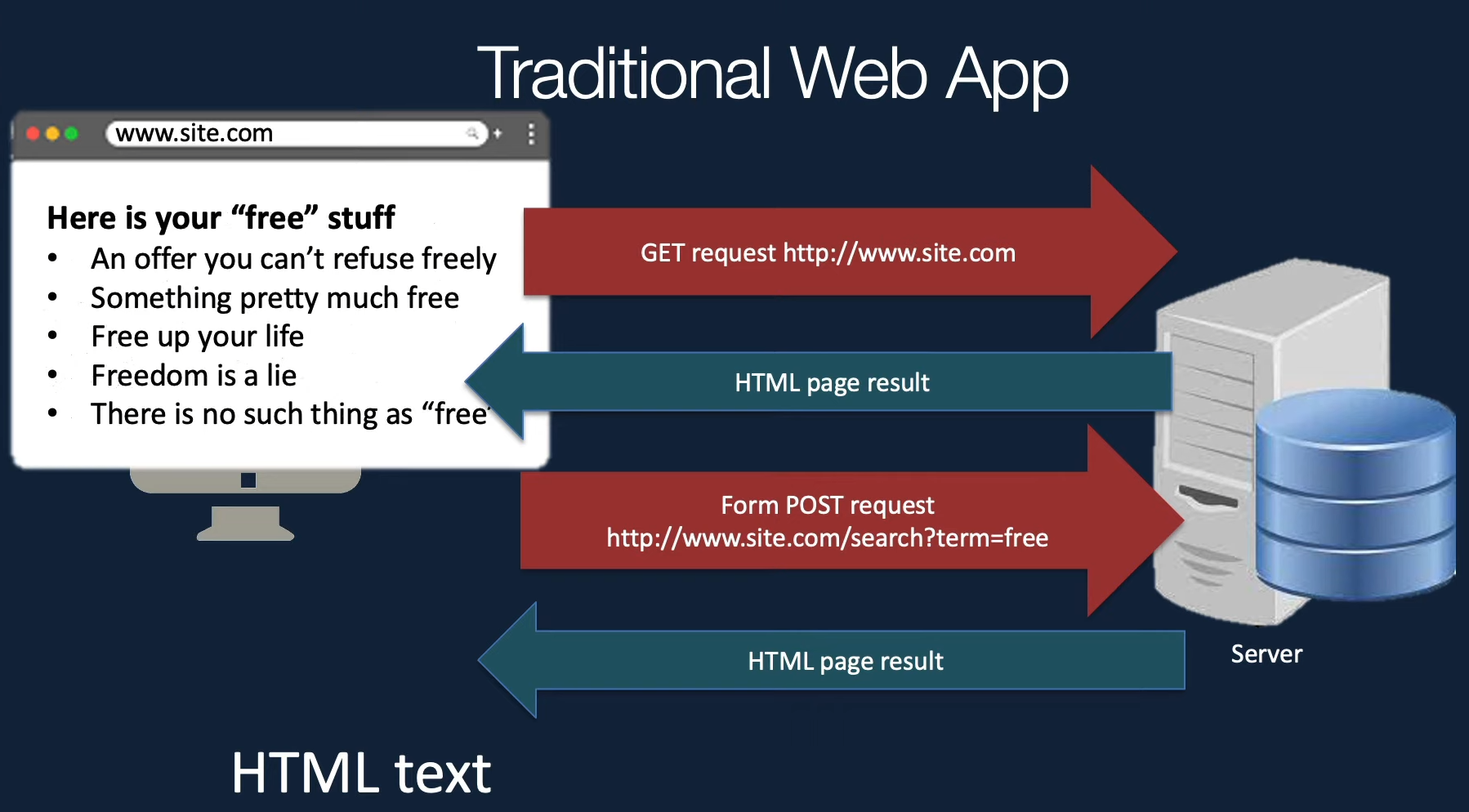
Tradional Web App
For each request, the server send back the whole page. The browser blanks out the page and render a new page.
Single Page Application (SPA)
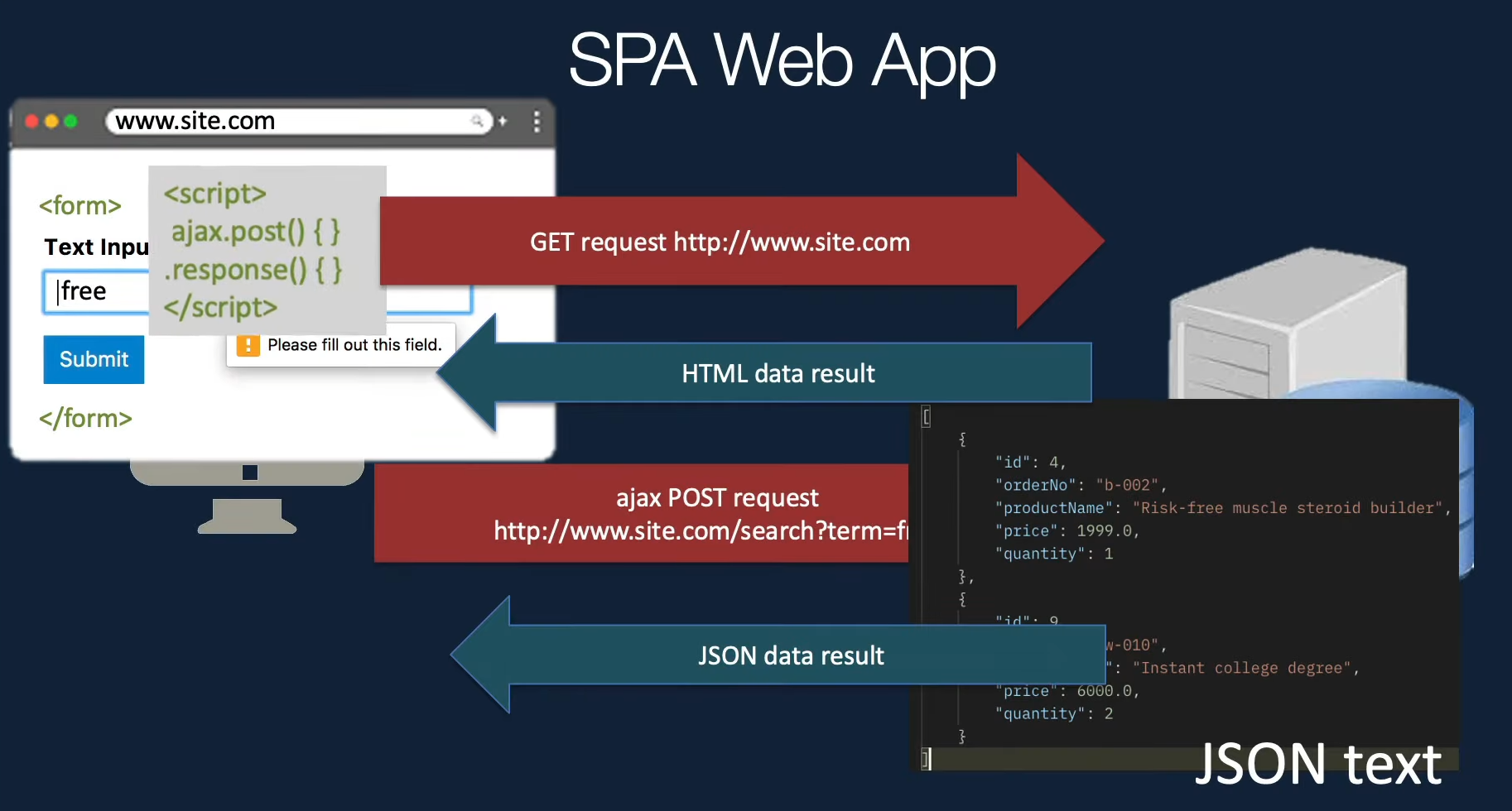
A single page application is a single page where a lot of information stays the same and only a few pieces need to be updated at a time. The SPA only sends what you need with each click, and your browser renders that information. This is different than a traditional page load where the server rerenders a full page with every click you make and sends it to your browser.
Test Driven Development
TDD is a technique where you define the behavior of your code before implementing it.
Lazy Loading
Process of loading components, modules, or other assets of a website only when they're required.
To lazy load Angular modules, use loadChildren (instead of component) in your AppRoutingModule routes configuration as follows.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'items',
// hilight-next-line
loadChildren: () => import('./items/items.module').then(m => m.ItemsModule)
}
];
Check out this article.
MVC & MVW
M - Model
Data that we work with
V - View
- HTML
- Display content and data to user
C - Controller
Control interaction between Model and View
W - Whatever
A bit flexibility