Introduction to AI
Definition of AI
Systems either displaying a behavior humans associate with intelligence or solving a problem humans think only an intelligent being can solve.
Criticize of the definition
- Subjective definition
- Changes over time
Graph of technology visibility
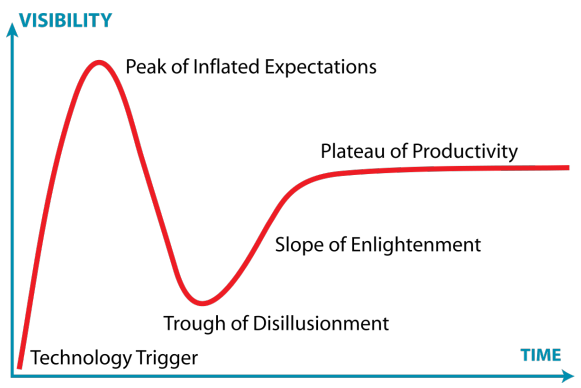
1. Tech trigger: new tech emerges, spark interest and media attention
2. Peak of Inflated Expectation: expectations skyrocket due to enthusiasm and speculation but tech often fail to meet these overblown expectations
3. Trough of Disillusionment: disappointment as implementation fail to deliver. Hype (visibility) diminishes significantly.
4. Slope of Enlightenment: Practical understanding grows and realistic use cases are identified.
5. Plateau of Productivity: tech becomes stable and widely adopted w tangible benefits
How does it relate to history of AI
1. Tech trigger: Early AI research (1950-60s) introduced foundational ideas leading to high hopes
2. Peak of Inflated Expectation: (1960-70s) immense optimism that AI would achieve human-like intelligence soon.
3. Trough of Disillusionment: When progress stalled due to computational limitations, lack of data, and unmet promises, funding was cut, leading to the first AI Winter (1970s-80s). A second AI Winter followed in the late 1980s and 1990s after disappointments with expert systems.
4. Slope of Enlightenment: Around the 2000s, machine learning, improved computing power, and large datasets began yielding practical applications, such as speech recognition and recommendation systems.
5. Plateau of Productivity: In recent years, AI technologies like deep learning and natural language processing (e.g., ChatGPT) are now widely adopted w tangible benefits
AGI
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a hypothetical form of artificial intelligence (AI) capable of understanding, learning, and applying knowledge.
- able to adapt and perform tasks not explicitly programmed for, like human intelligence
Criticize
All current AI cant do that. For example, the AlphaGo AI is programmed to play AlphaGo. It can play another game but its still a game not sth its not programmed to do.
How does it relate to AI?
It contrasts with AI (Artificial Intelligence), which typically focuses on specific tasks, like image recognition or language translation. AGI aims to replicate general cognitive abilities, while current AI is narrow, excelling in specific areas but lacking broader intelligence.
What are the 4 quadrants of historical AI areas?
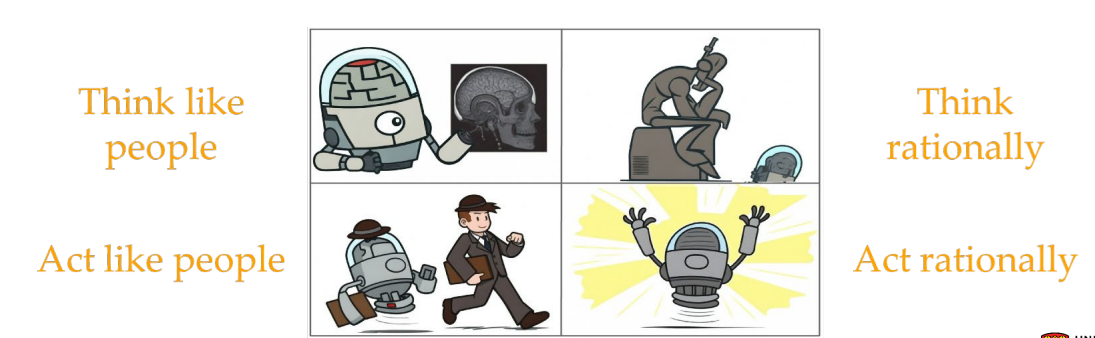
Act Rational
- Maximally achieving pre-defined goals
Acting Human
- Turing test aka Imitation Game: a machine and a human are behind the wall. The tester chat with both of them and rate if he/she is chating with a human or a machine. If similar, => acting human
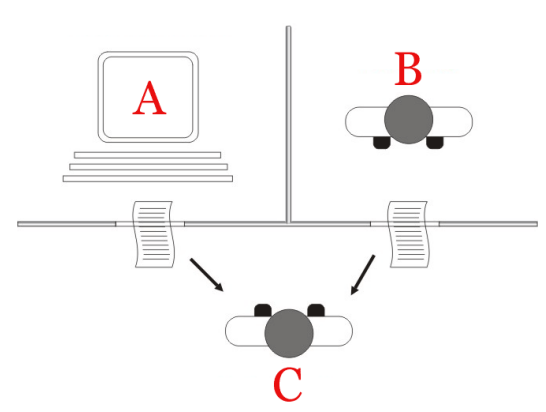
What is Imitation Game? Who defined it? Do we use it for consciousness testing? When?
- Its Turing test defined by Alan Turing. While it tests for intelligence, it is not designed for testing consciousness. It's more about the machine's ability to simulate intelligent behavior convincingly. It has been used in AI research and competitions
Think humanly
- information-processing psychology replaced behaviourism
- not yet there
Think rationally
Law of Thought
Principles of logic that guide rational thinking, often originating from Aristotle and Greek philosophers. These are normative (prescriptive) rules that describe how people should think to make correct arguments or decisions, rather than how people actually think (descriptive).
Act rationally
- Act such that maximize goal achievement
- Acting rationally doesn't always require deep thought or reasoning. For example, an automatic reflex, like blinking when something approaches your eyes, is a rational action to protect yourself. While it doesn't involve thinking, it still contributes to a goal (e.g., protecting the eye).
? What do we mean by AI being able to be defined as Computational Rationality?
AI systems using computation and logic to select the best actions that lead to the achievement of specific goals, based on the data and algorithms available to the system.
Agent
An agent is an entity that perceives and acts.
What is a rational agent?
A rational agent selects actions that maximize its (expected) utility.
Weak AI
Machines could act as if they were intelligent (pass Turing test)
Strong AI
Machines that do so are actually consciously thinking (not just simulating thinking)
Argument against AI
Argument from informality
human behaviour is far too complex to be captured by any formal set of rules
Argument from disability
“a machine can never do X.”
Polite Convention
if the machine could visibly act like a human, then the action or the behavioral test of looking like a human and tricking people, is sufficiently equivalent to a human, convincing people. You're human.
Chinese Room
- A human, who understands only English, inside a room that contains a rule book, written in English, and various stacks of paper
- Pieces of paper containing indecipherable symbols are slipped under the door to the room
- The human follows the instructions in the rule book, finding symbols in the stacks, writing symbols on new pieces of paper, rearranging the stacks, and so on passed back to the outside world
- The human does not understand Chinese
→ computer are in essence doing the same thing, so therefore computers generate no understanding